-


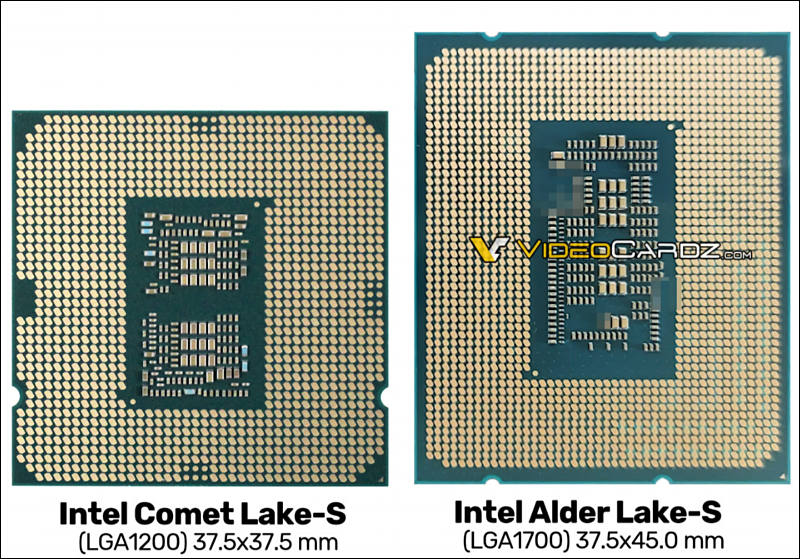
- LGA1700 socket (again, each year will be new socket!)
- 45 × 37,5mm size
- PCIe 4.0 or even PCIe 5.0 support
- DDR5 SDRAM
- 4 channel memory support possible
-
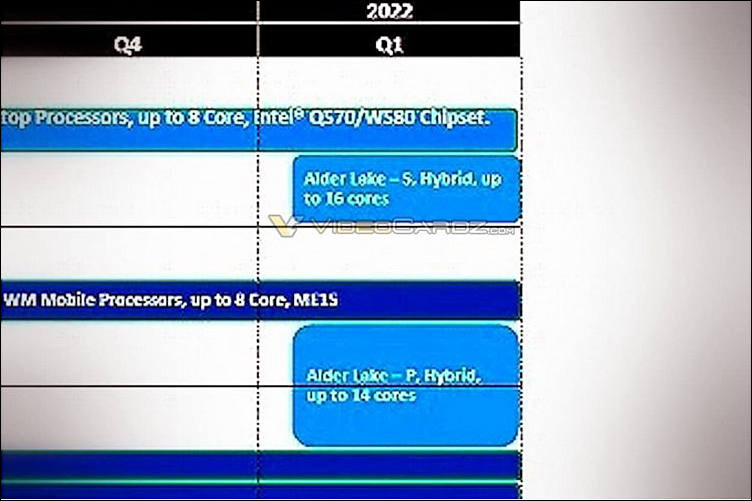
First leaks about Intel impotency
- 10nm (that still does not work normal for now)
- Large (normal) and small (Atom like) cores
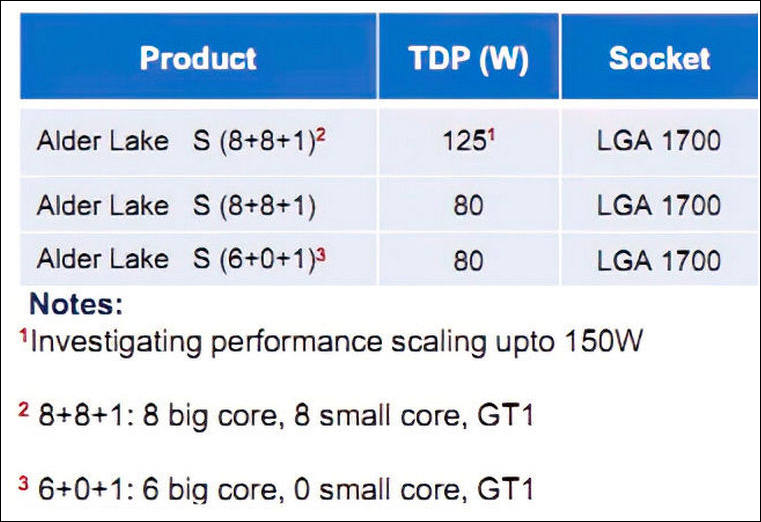
- TDP up to 125 watts, less capable models will be 80 watts

 sa12461.jpg761 x 522 - 62K
sa12461.jpg761 x 522 - 62K -
Screenshot of some dvelopers doc page, so it is LGA 1700 for certain.

 sa13504.jpg745 x 445 - 49K
sa13504.jpg745 x 445 - 49K -
Alder Lake-P (notebook chips)
- 6/12 Golden Cove CPU cores
- 8/8 Gracemont Low Power Atom class CPU cores
- 10m CPU and 14nm PCH in one package, 50x25mm
- PCIe CPU - Gen5 x8 + 2x Gen4 x4
- PCIe PCH - Gen3 x12
- 24MB LLC Cache
- GPU - Xe 96 EUs, 4x Display-out, DisplayPort 1.4b; AV1 accelerated encode; GNA 3.0
- DDR4-3200 up to 64 GB support, DDR5-4400 up to 64 GB support
- 4x Thunderbolt 4 + 1x Maple Ridge IO
- Wi-Fi 6E 802.11axR2
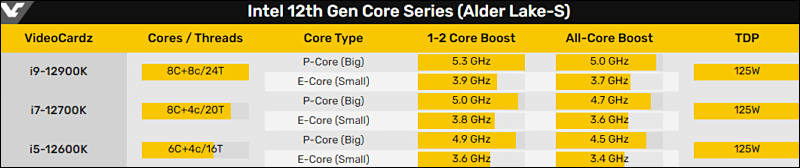
Alder Lake-S (desktop chips, can be used in gamers notes)
- 8/16 Golden Cove CPU cores
- 8/8 Gracemont Low Power Atom class CPU cores
- BGA option, Intel can start offering soldered CPUs for desktops
- 10m CPU 45mm x 37.5mm and 14nm PCH 28mm x 25mm, separate
- PCIe CPU - Gen5 x16 + Gen4 x4
- PCIe PCH - Gen4 x16 + Gen3 x12
- 30MB LLC Cache
- GPU - Xe 32 EUs, 4x Display-out, DisplayPort 1.4b; AV1 accelerated encode; GNA 3.0
- DDR4-3200 up to 128 GB support, DDR5-4400 up to 128 GB support
- 2x Maple Ridge IO
- Wi-Fi 6E 802.11axR2
- TDP up to 125 W
-
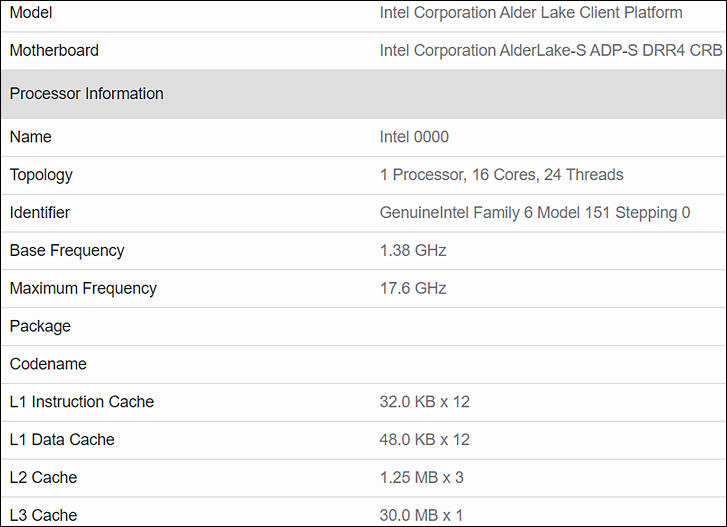
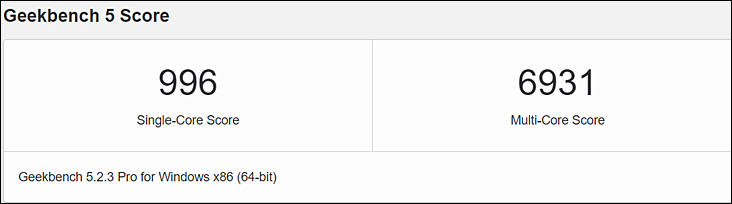
Geekbench


 sa16040.jpg727 x 527 - 57K
sa16040.jpg727 x 527 - 57K
 sa16043.jpg732 x 204 - 18K
sa16043.jpg732 x 204 - 18K
 sa16039.jpg743 x 396 - 91K
sa16039.jpg743 x 396 - 91K -
On mobile ones
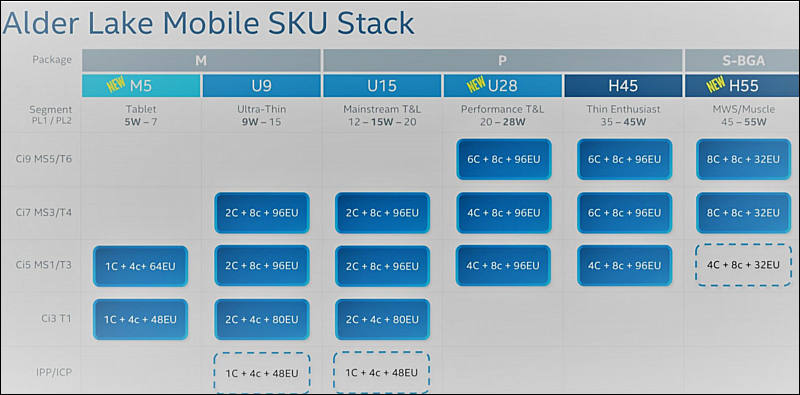
- Intel M5 – 5W-7W chips for tablets with Lakefield-like 1 big + 4 small core designs and 48 or 64 GPU execution units
- Intel U9 – 9W – 15W chips for ultra-thin laptops including 2 big + 4 or 8 small cores and 80eu or 96 eu graphics (there may also be a 1 big + 4 small + 48eu chip in this range)
- Intel U15 – 12W/15W/20W mainstream laptop chips with similar properties to the U9, but higher power consumption (and presumably higher clock speeds)
- Intel U28 – 20W – 28W “performance” chips with either 4 big + 8 small or 6 big + 8 small cores and 96eu graphics
- Intel H45 – 35W – 45W “thin enthusiast” chips for gaming laptops and workstations with 4 big + 8 small or 6 big + 8 small CPU cores + 96eu graphics
- Intel H55 – 45-55 watt processors with 8 big and 8 small cores + 32eu graphics, likely because these chips are designed for “muscle laptops” where they’ll be paired with discrete graphics (there may also be a 4 big + 8 small core version)

 sa17634.jpg800 x 395 - 58K
sa17634.jpg800 x 395 - 58K -
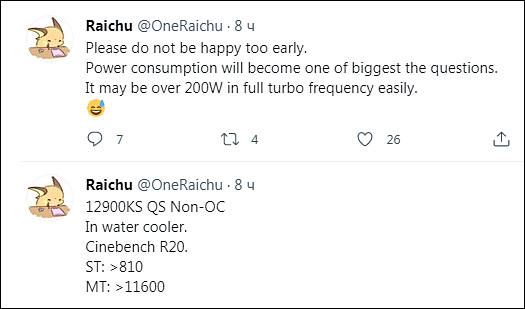
Very big power consumption
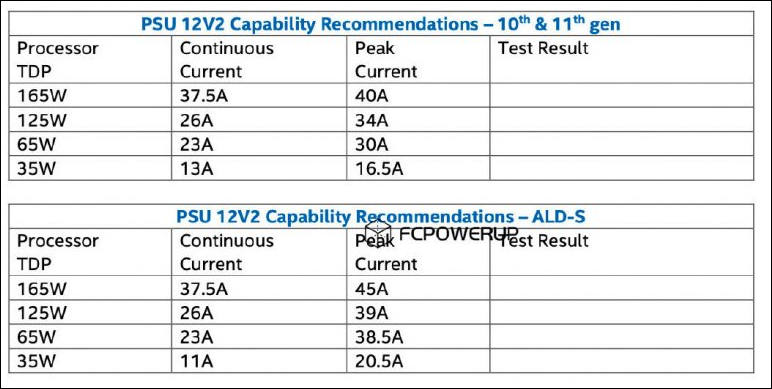
The Chinese portal FCPOWERUP, shared interesting information, taken, apparently, from Intel documentation for power supply manufacturers. It describes the power supply requirements for systems based on the new 12th Gen Intel Core processors, and specifies the constant and peak power values that the PSU must supply over a 12-volt power line for stable operation of Alder Lake chips with different TDP levels.
The documentation lists the requirements for processors with TDPs of 165, 125, 65 and 35 W. At the moment, there is no confirmation that Intel is going to use a hybrid architecture in HEDT processors, so chips with a TDP of 165W may not appear on the market at all. It is more important to pay attention to the requirements for processors with different power consumption indicators.
While the current requirements under continuous loads for 12th Gen Intel Core chips generally remained at the same level as for the current 10th and 11th Gen Core models for the LGA 1200 platform, the requirements for peak current values have increased markedly ... For Alder Lake models with a TDP of 125 W, the PSU should supply a maximum current of 39 A (468 W) on the 12-volt line in short-term mode, and not as before 34 A (408 W). For models with a TDP, this value increased from 30 A (360 W) to 38.5 A (462 W). And even the energy efficient 35W TDP models require the PSU to be able to deliver 20.5A (246W) peak loads. Thus, for 125-watt Alder Lake models, the required power supply of the PSU increased by 15%, and for models with a TDP of 65 and 35 W - by 28 and 24%, respectively.
This means that problems with the use of Alder Lake-S chips in theory can arise in systems that use old PSUs with multiple power lines (Multi-Rail). In these, the current on each individual line is typically limited to 20 A.

 sa17922.jpg772 x 389 - 55K
sa17922.jpg772 x 389 - 55K -
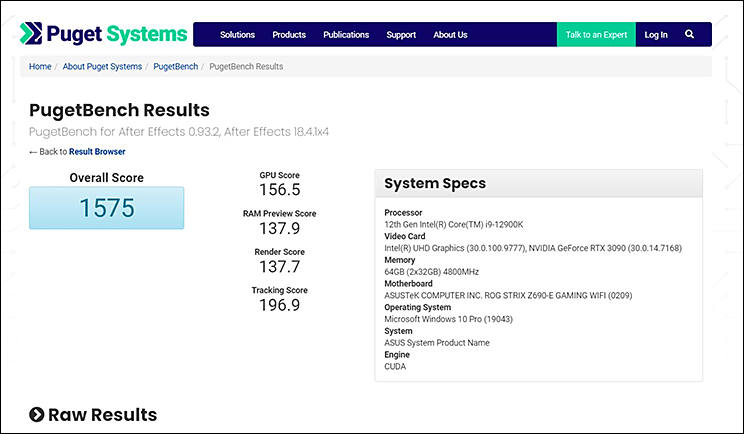
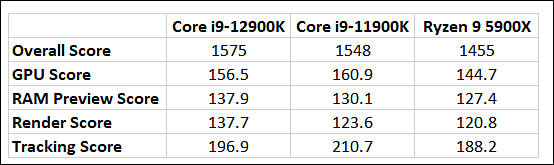
PurgetBench for After Effects

 sa18048.jpg744 x 434 - 42K
sa18048.jpg744 x 434 - 42K
 sa18049.jpg554 x 165 - 28K
sa18049.jpg554 x 165 - 28K -
Sources confirm that Intel's 12th Gen Core processor lineup, along with Z690 motherboards, will be available on November 19.
-
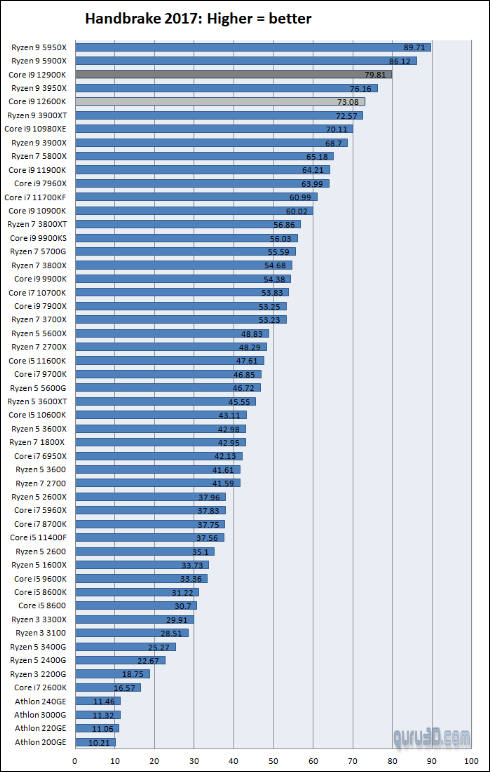
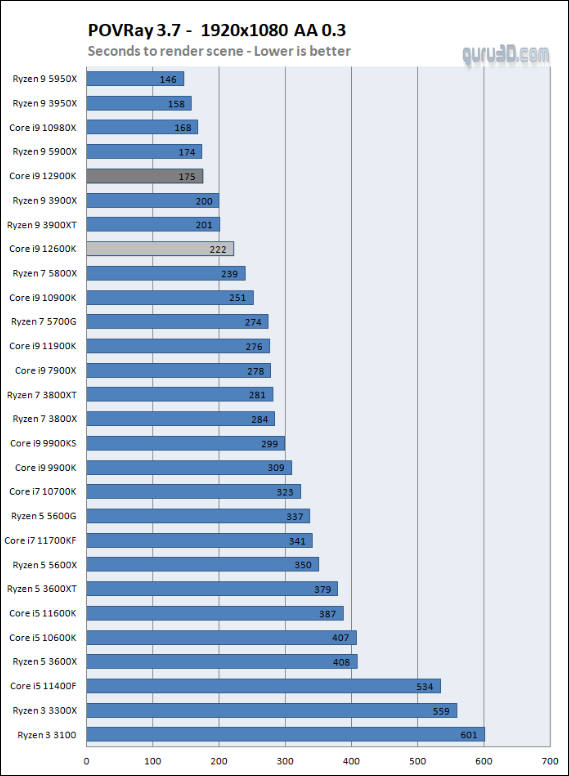
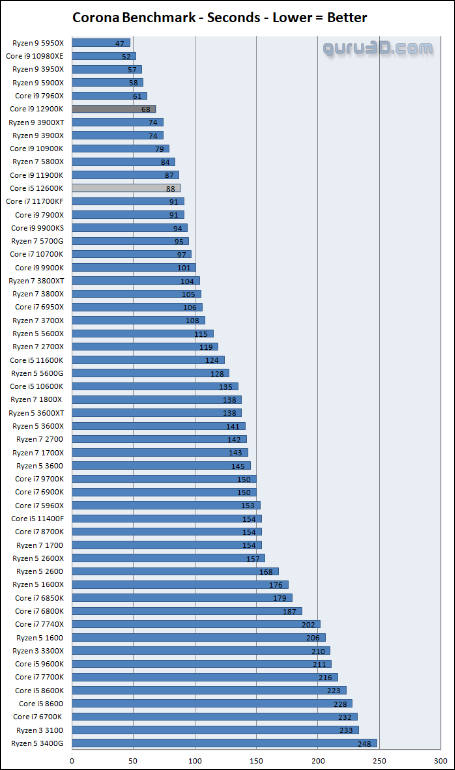
Some benchmarks
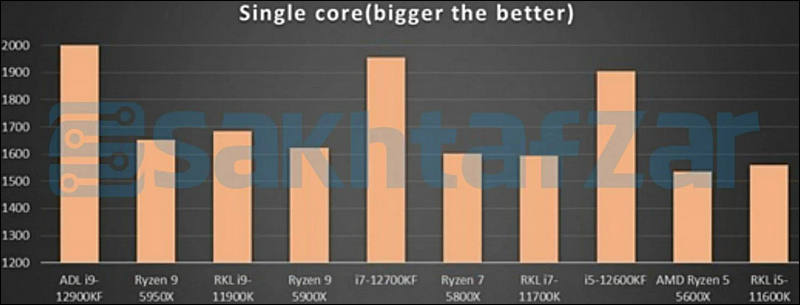
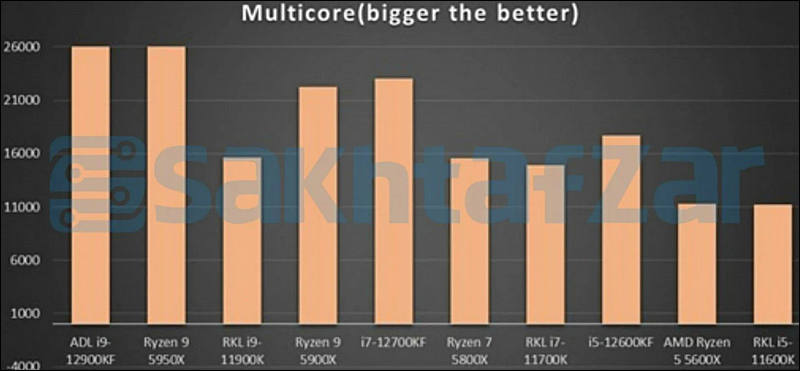
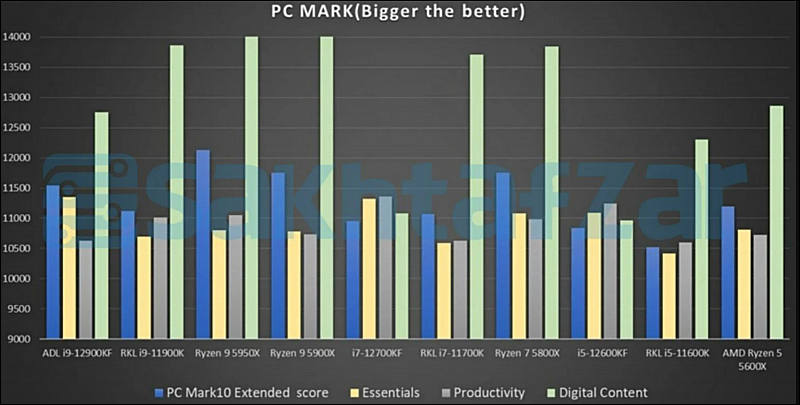
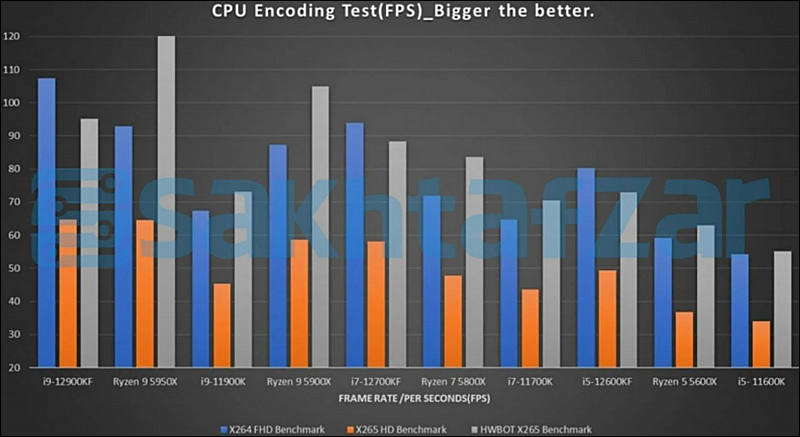

 sa18227.jpg800 x 305 - 32K
sa18227.jpg800 x 305 - 32K
 sa18228.jpg800 x 371 - 38K
sa18228.jpg800 x 371 - 38K
 sa18229.jpg800 x 405 - 55K
sa18229.jpg800 x 405 - 55K
 sa18230.jpg800 x 437 - 50K
sa18230.jpg800 x 437 - 50K -
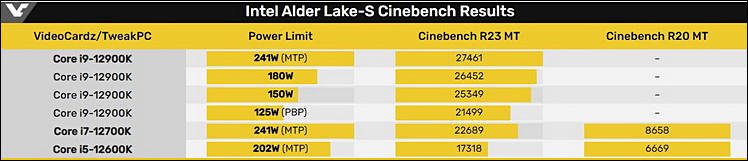
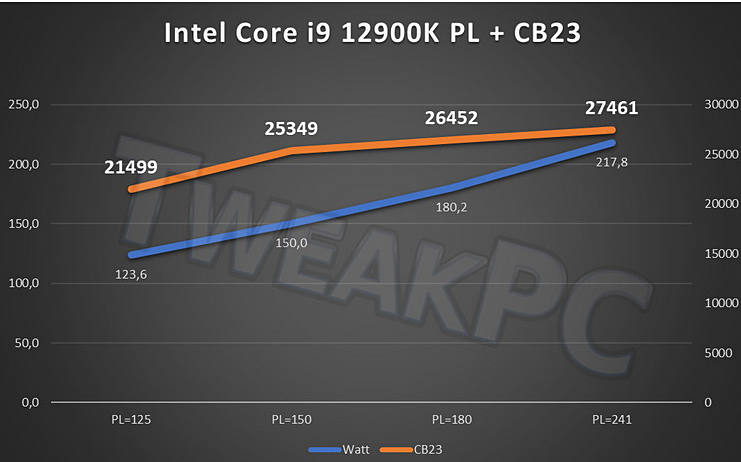
A sample of the upcoming flagship 16-core Intel Core i9-12900K processor of the Alder Lake generation turned out to be noticeably more productive than the 16-core AMD Ryzen 9 5950X flagship processor in the multi-threaded test of the Cinebench R23 benchmark.
Despite the difference in the number of threads, the Intel processor was able to outperform the AMD solution. The Core i9-12900K scores 30,549 points, while the Ryzen 9 5950X scores 25,586 points in this test. The current flagship Intel Core i9-11900K scores 15,325 points in the same test.
-
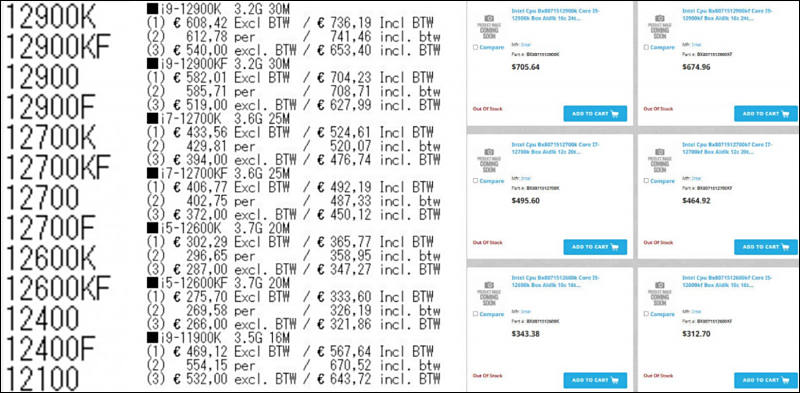
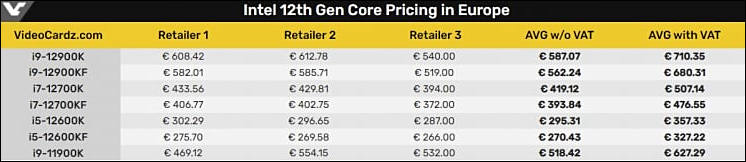
Core i9-12900K price will be $699
This chip will have a 3.2GHz operating frequency, capable of 5.2GHz in Turbo Mode, with 16 cores and 30MB of L3 cache. As expected, the specs reveal it also supports DDR5 memory, PCIe Gen 5, and the Intel Z690 chipset motherboards that should go on sale at the same time.
-

 sa18681.jpg490 x 772 - 91K
sa18681.jpg490 x 772 - 91K
 sa18682.jpg569 x 776 - 74K
sa18682.jpg569 x 776 - 74K
 sa18683.jpg455 x 770 - 82K
sa18683.jpg455 x 770 - 82K
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Categories
- Topics List24,002
- Blog5,724
- General and News1,368
- Hacks and Patches1,153
- ↳ Top Settings33
- ↳ Beginners255
- ↳ Archives402
- ↳ Hacks News and Development56
- Cameras2,365
- ↳ Panasonic990
- ↳ Canon118
- ↳ Sony155
- ↳ Nikon96
- ↳ Pentax and Samsung70
- ↳ Olympus and Fujifilm100
- ↳ Compacts and Camcorders299
- ↳ Smartphones for video97
- ↳ Pro Video Cameras191
- ↳ BlackMagic and other raw cameras123
- Skill1,961
- ↳ Business and distribution66
- ↳ Preparation, scripts and legal38
- ↳ Art149
- ↳ Import, Convert, Exporting291
- ↳ Editors191
- ↳ Effects and stunts115
- ↳ Color grading197
- ↳ Sound and Music280
- ↳ Lighting96
- ↳ Software and storage tips267
- Gear5,414
- ↳ Filters, Adapters, Matte boxes344
- ↳ Lenses1,579
- ↳ Follow focus and gears93
- ↳ Sound498
- ↳ Lighting gear314
- ↳ Camera movement230
- ↳ Gimbals and copters302
- ↳ Rigs and related stuff272
- ↳ Power solutions83
- ↳ Monitors and viewfinders339
- ↳ Tripods and fluid heads139
- ↳ Storage286
- ↳ Computers and studio gear560
- ↳ VR and 3D248
- Showcase1,859
- Marketplace2,834
- Offtopic1,324