
-
"Innovations" in refrigerators common for almost all of them
- Using of aluminium tubes in cooling and heating part of radiator, new ones use specially thin ones,
- Reason - good and with proper thickness copper tube will work >50 years perfectly, not good
- Aluminium allows to have controlled degradation at 10-15 years tops, but also not good
- Best is to use small part of copper tube near compressor and connect it with aluminium tube, this connection usually breaks in 4-5 years
- Covering top section evaporation radiator (aka crying wall) with foam, so corrosion and leak are very hard to find and costly to repair.
- Cheaper and simpler Chinese compressors used by most brands with savings on lot of stuff, including copper and other materials
- Another "smart" idea is to use less oil or very bad construction that dramatically shortens its life
- Directly related to point above - intentionally bad cooling of compressors
- Changing of simpler and better R12 (aka horrible ozone destructor) to modern more expensive and less fit for purpose R600a
- Read about Ozon Hoax using search on PV
- Advanced fully custom controllers that almost no one uses after setting, both DC power board and controllers have caps that like to die in 3-6 years.
- Lack of any sensors and logic that allows to really prolong refrigerator life, like oil level meter, freon pressure meter and compressor internal temperature
- Buttons and screens like to break
- Manufacturers do not like now to use simple bimetallic switch, as if one right it can function same 30-50 years.
- Bad plastic shelves that break easy and don't last long
- Good ones are metal, best ones are non painted stainless steel ones.
- Using of aluminium tubes in cooling and heating part of radiator, new ones use specially thin ones,
-
On copper
Copper as a metal has highly anti-corrosive properties compared to aluminium. During the cooling process, pipes comes in contact with air which causes oxidation within these pipes. Copper can better handle oxidation and corrosion for longer periods ultimately gives air conditioners a longer lifespan.
Cooling on copper pipes is much faster due its lower specific heat quality. The term ‘specific heat’ describes the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise temperature by one degree celsius. Lower the specific heat quantity, better the heating up and cooling down capabilities. As copper pipes have low specific heat quantity, they can rapidly dissipate heat into external environments and cool down quickly to absorb more heat. As aluminium pipes require more time to heat and cool down, they consume more energy and have comparatively lower cooling effectiveness.
Aluminium is fragile compared to copper. Due to copper’s less ductile nature, copper pipes are stronger and can easily withstand minor accidental damages. Even in case of cracks or punctures, copper pipes can be easily soldered. As aluminium pipe are fragile, soldering or repairing them is a chore and is better replaced.
Pricing of products is a crucial aspect, right? Copper is more expensive than aluminium. Due to copper pipes less ductile nature, the quantity of piping material required is also high, which makes copper-piped radiators a more expensive choice. Aluminium is cheaper and also more bendable so less material is required.
-
ATLANT totalitarian Belorus compressors, considered best and most silent among entry and some mid level here.
All else usually extremely cheapened China.
-
China makes the best stuff. How dare you criticize Xi Corp?
-
China makes the best stuff. How dare you criticize Xi Corp?
China makes cheap compressors for developing countries and entry level models, but they also do ones used in most premium refrigerators. So it all depends on that you need.
-
Refrigerators, which are currently sold in stores, are designed by the manufacturer for 5 years work time, I would even say that they are guaranteed to work only during the warranty time - 1-3 years, and they do not always succeed in this. Moreover, the reliability of modern refrigerators does not depend on their price, not on the manufacturer, or on the design of the refrigerator. Here there is a conspiracy of manufacturers of household appliances.
Otherwise, how can one explain the fact that old refrigerators work for 20-50 years without a single breakdown, withstanding numerous moves and extreme conditions at our dachas with high humidity and power drops. Whereas, modern refrigerators cannot step over a 10-year service life, not to mention periodic breakdowns throughout the entire operating period. Older refrigerators had a simpler design, fewer parts, and therefore less chance of breaking. In part, this is true.
Why was the quality of refrigerators better before? It is simply less profitable for the manufacturer to make good refrigerators! Refrigerators from the 90s were of much better quality than modern ones. The main indicator of the quality of the refrigerator, first of all, is the service life, many refrigerators of those years continue to work to this day.
During the repair process, you can evaluate the refrigerator from the inside, you can see everything that the consultants in stores do not know and the refrigerator manufacturers do not say.
- The thickness of the tubes through which freon circulates has significantly decreased.
- Copper tubes were replaced with steel and aluminum.
- The thickness of the plastic parts and coatings inside the refrigerator has been reduced to absolute minimum, now it can burst even from a heavy saucepan. Plastic frames for refrigerator shelves, drawers, door shelves and refrigerator handles are also made of thin, fragile plastic.
- Compressors, electronic modules, sensors, fans of modern refrigerators also have a minimum safety margin.
Modern technologies are aimed primarily at reducing the cost of the process of manufacturing refrigerators, and in no way at ensuring their reliability and long-term operation. The most noticeable deterioration in the quality of manufactured refrigerators began after 2004-2005, therefore refrigerators purchased earlier are of good quality. Summing up, I can say that the quality of refrigerators that was the standard 20-30 years ago is now unattainable for a modern refrigerator.
-
How innovations look like in refrigerators world
Sample of same size refrigerator made by same company within years. This guys defeated laws of physics.
Note that actual compressor efficiency actually did not change (contrary to marketing claims).
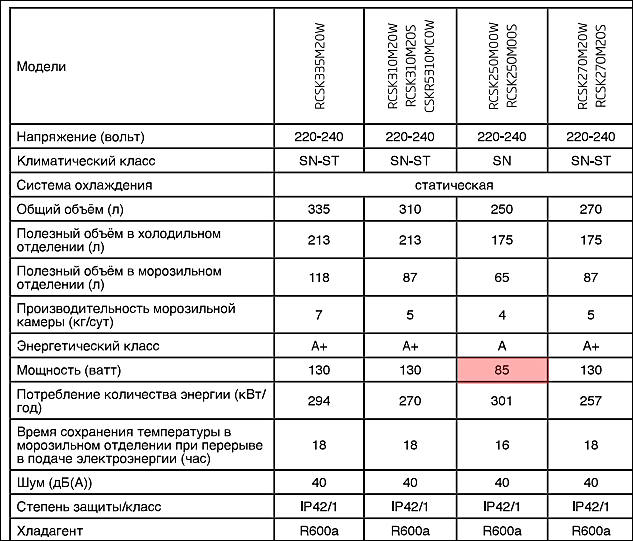
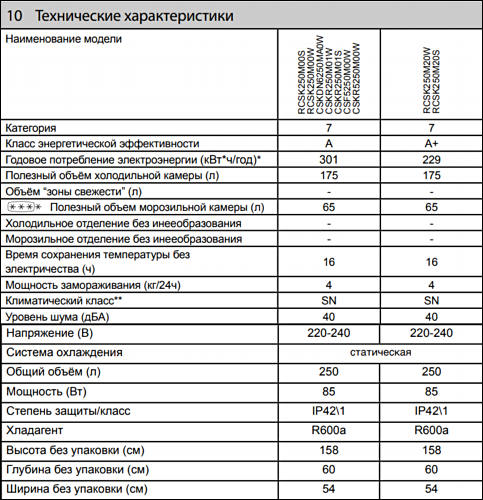
Iteration 1
250 liters freezer, used 134 watt (115×1,163) compressor with copper winding. Such compressor power is normal for such internal size.
Internal and condenser copper tubes, big rear condenser.

Iteration 2
Same model with new name, moved to 110w compressor with copper winding.
Internal and condenser aluminium tubes, big rear condenser.

Iteration 3
Slight changes with same size, moved to 85w compressor with aluminium winding. And it is fun as such compressor must work almost without pauses with any real load. Hence overheating and warrantied death within 4-5 years. Most probably within 3.
Internal and condenser thinner aluminium tubes, 50% smaller rear condenser.
How many managers saved on all this? Not too much, below $30-35 by reducing actual working life by at least 2-3 times. So, now you actually pay 1.9-2.8x times more for same time of having functioning refrigerator.
Iteration 4
Making fake A+ refrigerator using same compressor, same insulation and exactly same casing. They may increase condenser, but it can bring 2-5% tops not 31% of efficiency gain, especially considering that compressor is extremely underpowered.

 sa15928.jpg650 x 424 - 41K
sa15928.jpg650 x 424 - 41K
 sa15929.jpg633 x 387 - 38K
sa15929.jpg633 x 387 - 38K
 sa15930.jpg633 x 541 - 77K
sa15930.jpg633 x 541 - 77K
 sa15937.jpg483 x 500 - 71K
sa15937.jpg483 x 500 - 71K -
Glass shelves - invention that destroy food for tens of billions USD per year
Glass shelves came from No Frost designs where they had good reason, especially than paired with top of the line designs with more fans and where you can set temperatures per zone.
As it had been moved into simple evaporator design it resulted into huge losses due to blocking of air transfer, such way that warm food has trouble cooling down and in some areas time to cool down to proper temperature is 4-5x time more.
The obstacles (shelves and/or products) slow down the air circulation in the central zone of the refrigerator and mildly influence the main air circulation along the walls. This is confirmed by the maximum values of air temperature: 8.2 C for an empty refrigerator without shelves and 9.1 C for an empty refrigerator with shelves and refrigerator loaded with products. The air temperature at the top of the refrigerator is about 5 C higher than the average air temperature, and therefore it is important to avoid placing sensitive products in this position
-
“Super” greenhouse gases will soon be phased down in air conditioners and refrigerators in the US. The Environmental Protection Agency yesterday proposed new rules to cut the use of the “super” pollutants used as refrigerants, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), by 85 percent over 15 years. Consumers likely won’t notice much of a difference with their appliances, but lawmakers are anticipating big benefits for the planet.
The EPA plans to determine a baseline for HFC production and consumption, and then set limits on companies making and importing HFCs. Those caps would become stricter over time. This is the agency’s first major new regulation taking on climate change under the Biden administration, and it makes good on a bipartisan commitment to regulate HFCs that passed in Congress last December as part of the pandemic relief bill.
Note how this slowly became "greenhouse gases" and "super pollutants ", as scientific prostitutes continue to push narrative that their owners ask them for.
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Categories
- Topics List23,964
- Blog5,723
- General and News1,342
- Hacks and Patches1,151
- ↳ Top Settings33
- ↳ Beginners254
- ↳ Archives402
- ↳ Hacks News and Development56
- Cameras2,361
- ↳ Panasonic990
- ↳ Canon118
- ↳ Sony154
- ↳ Nikon96
- ↳ Pentax and Samsung70
- ↳ Olympus and Fujifilm99
- ↳ Compacts and Camcorders299
- ↳ Smartphones for video97
- ↳ Pro Video Cameras191
- ↳ BlackMagic and other raw cameras121
- Skill1,961
- ↳ Business and distribution66
- ↳ Preparation, scripts and legal38
- ↳ Art149
- ↳ Import, Convert, Exporting291
- ↳ Editors191
- ↳ Effects and stunts115
- ↳ Color grading197
- ↳ Sound and Music280
- ↳ Lighting96
- ↳ Software and storage tips267
- Gear5,414
- ↳ Filters, Adapters, Matte boxes344
- ↳ Lenses1,579
- ↳ Follow focus and gears93
- ↳ Sound498
- ↳ Lighting gear314
- ↳ Camera movement230
- ↳ Gimbals and copters302
- ↳ Rigs and related stuff272
- ↳ Power solutions83
- ↳ Monitors and viewfinders339
- ↳ Tripods and fluid heads139
- ↳ Storage286
- ↳ Computers and studio gear560
- ↳ VR and 3D248
- Showcase1,859
- Marketplace2,834
- Offtopic1,319




